As energy technologies continue to advance, battery technology, as a key factor driving modern technological development, has always been a topic of wide attention. Among the many battery technologies, lithium-ion batteries have become one of the most widely used types today, finding applications in electric vehicles, portable devices, and energy storage systems. However, with increasing demand and the emergence of technological limitations, researchers have turned their focus to the development of new battery technologies, one of which is the semi-solid state battery. This article will explore the differences, advantages, and challenges between semi-solid state batteries and lithium-ion batteries in four aspects: architecture, performance, technological features, and practical applications.
1. Overview of Lithium-Ion Batteries
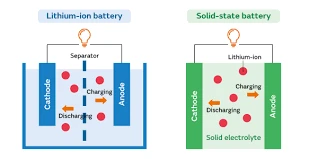
Lithium-ion batteries have become the mainstream of modern battery technology since they were first commercialized in 1991. Known for their high energy density, long lifespan, and lightweight, they are widely used in mobile phones, laptops, and other portable devices. In lithium-ion batteries, energy is stored and released through the intercalation and de-intercalation of lithium ions. During charging, lithium ions move from the positive electrode (typically lithium cobalt oxide or nickel-cobalt-manganese oxide) to the negative electrode (usually graphite), and during discharge, they move in the reverse direction.
Advantages:
- High Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries have relatively high energy density, providing more energy in the same volume and weight.
- Long Cycle Life: Lithium-ion batteries have a long charging and discharging lifespan, typically ranging from hundreds to thousands of cycles.
- Widespread Application: Due to their superior performance, lithium-ion batteries are widely used in mobile phones, laptops, electric vehicles, and other fields.
Disadvantages:
- Safety Issues: Lithium-ion batteries have safety concerns, as extreme conditions (e.g., overcharging, overheating, or damage) can lead to thermal runaway, causing fire or explosion.
- Energy Degradation: Over time, the battery's energy capacity degrades, and the charging speed is relatively slow.
- Environmental Impact: The production process and disposal of lithium-ion batteries may have environmental impacts, especially concerning the toxic metals used in their materials.
2. Overview of Semi-Solid State Batteries
A semi-solid state battery is a new type of battery technology that combines the advantages of solid-state batteries and traditional liquid-based batteries. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, semi-solid state batteries use a viscous electrolyte, often made of a gel or semi-liquid substance, instead of the traditional liquid electrolyte. While there are differences in the electrolyte, the overall structure of a semi-solid state battery is similar to that of a lithium-ion battery, which is why it is considered a transitional technology toward solid-state batteries.
Advantages:
- Higher Safety: Due to the use of a viscous or semi-solid electrolyte, semi-solid state batteries are inherently safer. Compared to liquid electrolyte lithium-ion batteries, the risk of leakage and thermal runaway is significantly reduced.
- Higher Energy Density: Semi-solid state batteries can offer higher energy density than traditional liquid batteries, making them ideal for high-performance applications such as electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
- Longer Lifespan: Semi-solid state batteries exhibit better performance in terms of cycle life and stability, with far superior charging and discharging cycles compared to lithium-ion batteries.
- Environmentally Friendly: Semi-solid state batteries are more eco-friendly, as their materials are more recyclable and have less environmental impact during manufacturing.
Disadvantages:
- High Production Cost: Due to the new technology and complex manufacturing processes, the production cost of semi-solid state batteries is currently higher, and their commercial applications are still limited.
- Immature Technology: Although semi-solid state batteries have shown promising results in laboratory experiments and initial applications, the overall technology is still being refined and requires further validation for reliability.
- Power Output Limitations: While semi-solid state batteries offer higher energy density, they are still under development in terms of high power output and fast charging speeds.
3. Comparison Between Semi-Solid State Batteries and Lithium-Ion Batteries
| Feature | Lithium-Ion Battery | Semi-Solid State Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | High, suitable for portable devices | Higher than lithium-ion batteries, ideal for high-performance applications |
| Safety | Some risks, such as thermal runaway | Higher safety, reduced risk of leakage and explosions |
| Cycle Life | Long, but degrades over time | Longer, suitable for high-load, long-cycle use |
| Charging Speed | Generally slow, with fast-charging technology in development | Charging speed is improving but still under development |
| Cost | Mass-produced, relatively low cost | High production cost, technology still in development |
| Environmental Impact | Greater environmental impact, especially in production | More eco-friendly, materials are more recyclable |
4. Future Prospects and Applications
Semi-solid state batteries, as an emerging technology, have great potential due to their safety, energy density, and environmentally friendly characteristics. While the commercialization process is still slow, semi-solid state batteries are expected to become the dominant battery technology in the future for electric vehicles, portable devices, and energy storage systems.
Lithium-ion batteries, despite their maturity and widespread use, have gradually exposed their shortcomings as the demand for higher performance and safety increases. As a result, semi-solid state batteries, with their potential advantages, are becoming a promising alternative.
Conclusion
Semi-solid state batteries and lithium-ion batteries each have their own advantages and challenges. While lithium-ion batteries dominate the current market, semi-solid state batteries, with their increasing maturity, are likely to revolutionize energy solutions in the future. Whether it is for electric vehicles, portable devices, or large-scale energy storage, semi-solid state batteries have the potential to bring about significant changes in our lives.


