The difference between polymer batteries and lithium batteries:
Polymer Battery: Lithium-ion polymer (LiPo) batteries (also known as Li-poly, Lithium-poly, PLiON) have similar electrode compositions to lithium-ion batteries, but the electrode material is applied in a gel-like or solid polymer matrix. This eliminates the need for porous separators and allows for greater flexibility in the battery's form factor. Polymer batteries are a type of battery that uses a solid or gel electrolyte, usually based on lithium-ion technology. Their main feature is the use of a solid or gel polymer electrolyte instead of a traditional liquid electrolyte.
Lithium Battery: Lithium-ion batteries consist of multiple cylindrical or prismatic cells, each of which contains a positive electrode (cathode), a negative electrode (anode), and a liquid electrolyte solution. A porous separator is placed between the cathode and the anode to allow lithium ions to move during charging and discharging. Lithium batteries refer to batteries that use lithium as the main electrode material, including lithium-ion batteries (lithium ferrite phosphate、Li-ion) and lithium polymer batteries (Lithium Polymer). Lithium batteries are usually designed to use liquid electrolytes.

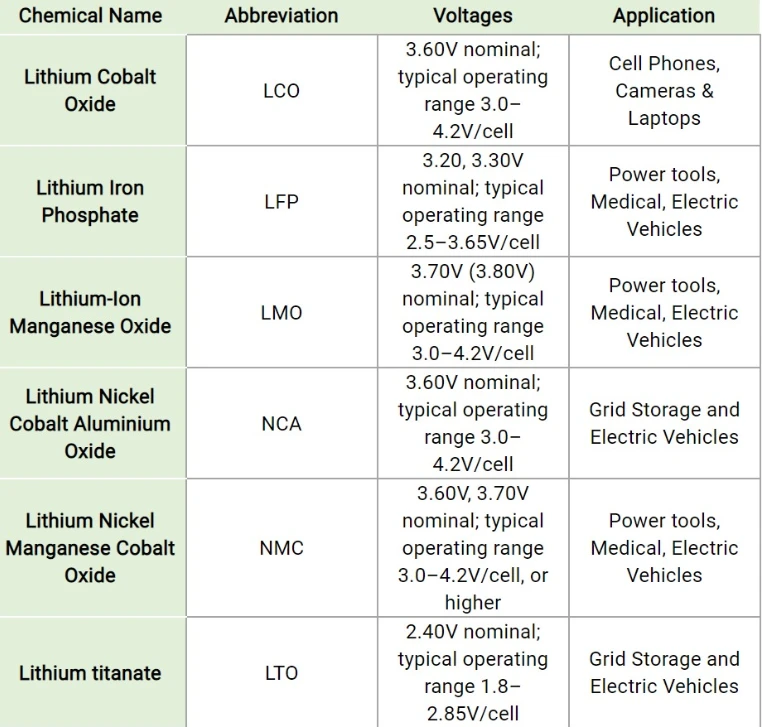
The table below compares the voltages and typical applications of six basic lithium battery chemistries. Other characteristics of these batteries include:
LCO – 200Wh/kg, provides high power, but at the expense of relatively short life, low power rating, and low thermal stability.
LFP – 120Wh/kg, has long cycle life and stability at high operating temperatures.
LMO – 140Wh/kg, cathodes are based on manganese oxide components, which are abundant, cheap, non-toxic, and provide good thermal stability.
NCA – 250Wh/kg, provides high specific energy and long cycle life.
NMC – 200Wh/kg, changing the ratio of chemical components can develop batteries optimized for power or energy cells. It is one of the most successful lithium battery chemistry systems due to its flexibility.
LTO – 80Wh/kg, lowest specific energy, but can be charged quickly, discharged at up to 10 times the rated capacity, and is safe.
NMC, LCO and NCA cells contain cobalt, which helps provide higher power capabilities. They can deliver a lot of power in a small package but are more susceptible to thermal events that can cause safety issues.
Advantages of polymer batteries and lithium batteries:
The main advantages of lithium polymer batteries are:
- Thinner, more flexible form factors - Polymer electrolyte allows the battery to be molded into a variety of forms
- Safer operation - Solid polymer electrolytes are less prone to leakage and thermal runaway than liquid electrolytes in lithium ion
- Longer cycle life - Li-polymer batteries can generally withstand more charge/discharge cycles
The main advantages of lithium ion batteries are:
- Higher energy density - They can store more energy per unit volume than lithium polymer
- Lower internal resistance - Leading to faster charge and discharge capabilities
- More mature and established technology - Li-ion batteries are more widely produced and available
As for which is "best", there is no clear winner as both technologies have their own advantages. The choice depends on the specific application and requirements. Li-polymer is better suited for portable devices that require thin, flexible form factors, while lithium-ion batteries are favored where energy density and power output are a priority, such as electric vehicles. Many modern devices may use a mix of the two technologies to take advantage of their respective strengths.
For more information, please contact us: ciclibattery.com


